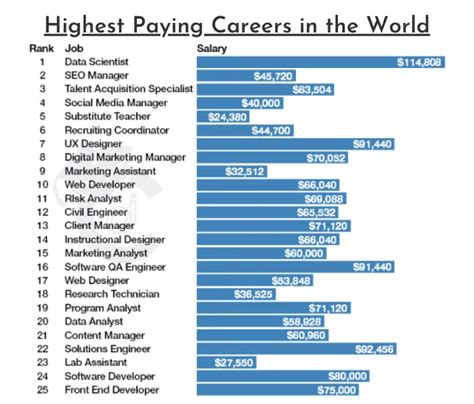
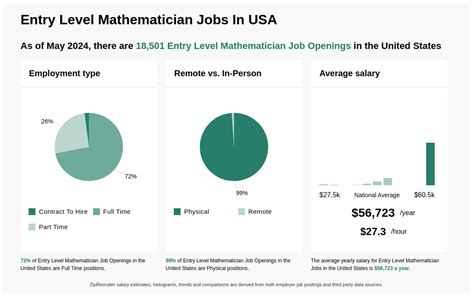
Mathematician Jobs

The field of mathematics is vast and encompasses a wide range of disciplines, from pure mathematics to applied mathematics, statistics, and computer science. As a result, the career opportunities for mathematicians are diverse and exciting. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the world of mathematician jobs, delving into the various roles, their responsibilities, and the skills required to excel in this field. From research to industry applications, we will uncover the fascinating paths mathematicians can embark on.
Research Mathematics: Unveiling the Mysteries of Numbers

One of the most traditional and revered paths for mathematicians is academia and research. Pure mathematicians dedicate their careers to exploring the fundamental principles and theories of mathematics. They delve into abstract concepts, develop new mathematical frameworks, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their specific field of interest.
Research mathematicians often specialize in areas such as algebraic geometry, number theory, topology, or mathematical physics. Their work involves tackling complex problems, proving theorems, and pushing the boundaries of mathematical understanding. These individuals are at the forefront of mathematical innovation, shaping the future of the discipline.
Skills and Responsibilities of Research Mathematicians
- Advanced mathematical knowledge and analytical skills.
- Ability to develop and communicate complex mathematical theories.
- Conduct research independently or as part of a team.
- Publish research findings in academic journals and present at conferences.
- Mentor and guide graduate students and junior researchers.
Educational Pathway
A career in research mathematics typically requires a strong academic foundation. Most research mathematicians hold at least a master’s degree, if not a PhD, in mathematics or a related field. Postdoctoral research positions are also common, allowing mathematicians to further specialize and gain recognition in their chosen area of expertise.
Applied Mathematics: Solving Real-World Problems
While pure mathematics focuses on abstract concepts, applied mathematics takes mathematical theories and applies them to solve practical problems in various industries. Applied mathematicians work closely with scientists, engineers, and other professionals to develop mathematical models and algorithms that address real-world challenges.
The applications of applied mathematics are vast, ranging from finance and economics to physics, biology, and computer science. For instance, applied mathematicians might develop optimization models for logistics and supply chain management, create mathematical models to predict stock market trends, or contribute to the development of machine learning algorithms for image recognition.
Skills and Responsibilities of Applied Mathematicians
- Strong problem-solving and analytical skills.
- Ability to apply mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios.
- Develop mathematical models and simulations.
- Collaborate with interdisciplinary teams.
- Interpret and communicate complex mathematical results to non-mathematicians.
Industries and Sectors
Applied mathematicians find employment opportunities in a wide range of industries, including:
- Finance and Insurance: Developing risk assessment models, portfolio optimization strategies, and quantitative trading algorithms.
- Engineering: Simulating physical systems, designing control systems, and optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Healthcare: Modeling disease spread, developing medical imaging algorithms, and optimizing healthcare resource allocation.
- Technology: Contributing to machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data science research and development.
- Energy and Environmental Sciences: Modeling climate change, optimizing renewable energy systems, and analyzing environmental data.
Data Science and Statistics: Unlocking Insights from Data
In today’s data-driven world, the demand for mathematicians with expertise in data science and statistics is soaring. These professionals are at the forefront of extracting valuable insights and knowledge from vast amounts of data. Whether it’s analyzing customer behavior for a marketing campaign or developing predictive models for healthcare outcomes, data scientists and statisticians play a crucial role in driving decision-making processes.
Skills and Responsibilities of Data Scientists and Statisticians
- Proficiency in statistical analysis and data modeling.
- Expertise in programming languages such as Python, R, or SQL.
- Ability to design and conduct experiments.
- Interpret and communicate data-driven insights to stakeholders.
- Develop machine learning algorithms and predictive models.
Industry Applications
Data scientists and statisticians are in high demand across various sectors, including:
- E-commerce and Retail: Analyzing customer data, optimizing pricing strategies, and personalizing marketing campaigns.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Developing clinical trial designs, analyzing medical research data, and improving patient outcomes.
- Financial Services: Risk assessment, fraud detection, and developing quantitative investment strategies.
- Social Media and Technology: Analyzing user behavior, optimizing content recommendations, and improving user experiences.
- Government and Policy: Conducting surveys, analyzing demographic data, and informing public policy decisions.
Mathematics Education: Nurturing the Next Generation
Mathematicians also play a vital role in education, both at the primary and secondary levels and in higher education institutions. Mathematics educators are responsible for imparting mathematical knowledge and skills to students, fostering their understanding and appreciation of the subject.
Skills and Responsibilities of Mathematics Educators
- Excellent communication and pedagogical skills.
- Ability to adapt teaching methods to different learning styles.
- Develop and deliver engaging mathematical lessons.
- Assess student progress and provide constructive feedback.
- Stay updated with the latest teaching methodologies and educational technologies.
Career Paths in Mathematics Education
Mathematics educators can pursue various career paths, including:
- Primary and Secondary School Teachers: Teaching mathematics to students from diverse backgrounds and age groups.
- College and University Instructors: Lecturing and mentoring undergraduate and graduate students.
- Educational Researchers: Conducting research on effective teaching strategies and curriculum development.
- Tutors and Mentors: Providing one-on-one or small group instruction to students seeking additional support.
- Curriculum Developers: Creating and designing mathematics textbooks, online courses, and educational resources.
Mathematics in Industry: A Multidisciplinary Approach
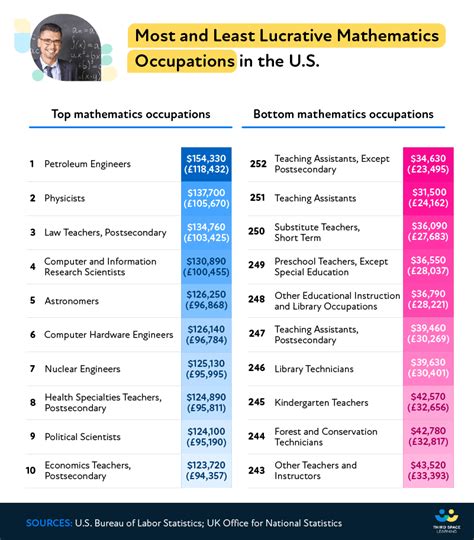
Mathematicians often find themselves working in multidisciplinary teams within various industries. Their expertise is highly valued in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and defense, where mathematical modeling and simulation play a critical role in product development and optimization.
For instance, mathematicians might collaborate with engineers to design and optimize aircraft structures, develop advanced materials, or simulate complex physical phenomena. In the field of operations research, mathematicians work with logistics and supply chain professionals to optimize distribution networks and enhance efficiency.
Skills and Responsibilities of Industry Mathematicians
- Strong mathematical and computational skills.
- Ability to communicate and collaborate with professionals from diverse backgrounds.
- Develop and implement mathematical models and simulations.
- Analyze and interpret data to inform decision-making.
- Stay updated with industry-specific software and tools.
Industry Sectors
Mathematicians find employment opportunities in a wide range of industries, including:
- Aerospace and Defense: Designing aircraft, simulating flight dynamics, and optimizing mission planning.
- Automotive: Developing advanced driver-assistance systems, optimizing vehicle performance, and improving fuel efficiency.
- Energy and Utilities: Modeling power grids, optimizing renewable energy systems, and analyzing energy consumption patterns.
- Healthcare Technology: Developing medical imaging algorithms, optimizing drug delivery systems, and improving patient monitoring.
- Financial Services: Risk management, algorithmic trading, and developing quantitative investment strategies.
Conclusion: A World of Opportunities
The field of mathematics offers an abundance of career opportunities, each with its unique challenges and rewards. Whether it’s the thrill of uncovering new mathematical theories, the satisfaction of solving real-world problems, or the joy of nurturing mathematical minds, mathematicians have the privilege of exploring and contributing to a wide range of disciplines.
As the world becomes increasingly reliant on data and mathematical models, the demand for mathematicians continues to grow. With their expertise and analytical skills, mathematicians are positioned to make significant contributions to society, driving innovation, improving efficiency, and shaping the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifications do I need to become a mathematician?
+To pursue a career in mathematics, a strong academic foundation is essential. Most mathematician roles require at least a bachelor’s degree in mathematics or a related field. For research and academic positions, a master’s or PhD is typically necessary. Additionally, proficiency in programming languages and data analysis tools is highly valued in many mathematician jobs.
What are the key skills required for a mathematician?
+Mathematicians possess a unique skill set, including advanced mathematical knowledge, analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and the capacity to communicate complex ideas effectively. Depending on the specific role, additional skills such as programming, data analysis, or industry-specific expertise may be required.
How do I choose between pure and applied mathematics?
+The choice between pure and applied mathematics often depends on individual interests and career aspirations. Pure mathematicians focus on developing abstract theories and pushing the boundaries of mathematical knowledge, while applied mathematicians apply mathematical concepts to solve real-world problems. Consider your passion and the type of work you find most fulfilling.
What are the career prospects for mathematicians in the job market?
+The job market for mathematicians is highly favorable, with a growing demand for their skills across various industries. Mathematicians with a strong academic background and practical experience are sought after in fields such as finance, data science, healthcare, and technology. The ability to adapt and acquire industry-specific knowledge further enhances career prospects.
How can I stay updated with the latest advancements in mathematics?
+To stay current with the latest advancements in mathematics, it is essential to engage in continuous learning and professional development. Attend conferences, workshops, and seminars related to your area of interest. Read academic journals, blogs, and books written by renowned mathematicians. Additionally, online platforms and communities dedicated to mathematics can provide valuable insights and networking opportunities.
Related Terms:
- mathematician jobs remote
- Entry level Mathematician jobs
- mathematician jobs no degree
- Mathematician jobs salary
- Mathematician jobs near me
- Mathematician jobs remote