Jobs To Be Done Framework
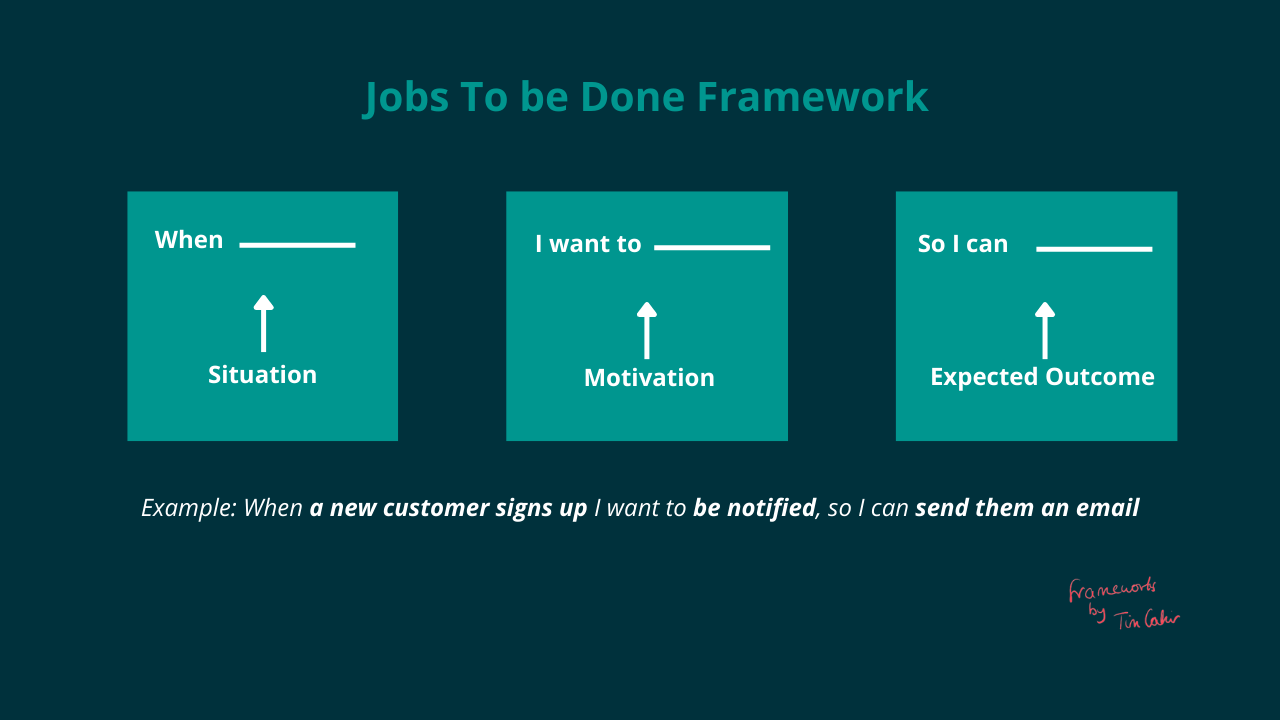
The Jobs To Be Done (JTBD) framework is a powerful and innovative approach to understanding consumer behavior and market opportunities. Developed by Tony Ulwick and popularized by Clayton Christensen and colleagues, this concept shifts the focus from product-centric thinking to a deeper understanding of the "job" or task that consumers are trying to accomplish. By unraveling the complex web of customer needs, desires, and motivations, the JTBD framework empowers businesses to create products and services that are not just desirable but indispensable to their target audience.
Understanding the Jobs To Be Done Framework

At its core, the JTBD framework revolves around the idea that consumers hire products or services to get a “job” done. This job could be anything from improving their productivity, achieving a specific goal, or addressing a pain point. By identifying these jobs, businesses can develop solutions that are tailored to meet these specific needs, rather than creating products and then trying to convince customers that they need them.
The framework proposes that every product or service is hired to perform a job, and this job is defined by the consumer's unique set of circumstances and goals. These jobs can be as varied as the consumers themselves, ranging from simple tasks like finding a quick snack to more complex endeavors like planning a wedding or launching a new business venture.
The beauty of the JTBD framework lies in its ability to delve into the consumer's mindset. It encourages businesses to ask probing questions like: What are the underlying motivations behind a consumer's actions? What problems are they trying to solve? What outcomes are they seeking? By answering these questions, businesses can design products and services that truly resonate with their target audience.
Key Components of the JTBD Framework
The JTBD framework consists of several key components that help businesses dissect the consumer’s journey and uncover hidden opportunities:
- Functional Jobs: These are the tasks that consumers want to get done. For instance, a functional job could be to clean a dirty kitchen or to create a professional-looking presentation.
- Emotional Jobs: These relate to the feelings and experiences consumers want to have. An emotional job might be to feel confident while giving a public speech or to experience the joy of a perfect family vacation.
- Social Jobs: These are tied to the consumer's social context and how they want to be perceived by others. A social job could be to impress colleagues with a cutting-edge presentation or to maintain a healthy lifestyle image on social media.
- Self-Image Jobs: These revolve around how consumers want to perceive themselves. For example, a self-image job could be to feel more organized and in control of one's life or to feel like a savvy investor.
By breaking down the consumer's journey into these distinct categories, businesses can develop a more holistic understanding of their target audience and create solutions that cater to these multifaceted needs.
The Process of Applying the JTBD Framework

Implementing the JTBD framework involves a series of systematic steps that guide businesses through the process of understanding their customers and developing innovative solutions:
Step 1: Identify the Job
The first step is to clearly define the job that the consumer is trying to accomplish. This involves in-depth research and customer interviews to understand their goals, pain points, and expectations. It’s crucial to go beyond surface-level responses and delve into the “why” behind their actions.
For instance, if a customer is looking for a new laptop, the job could be to improve their productivity by having a faster and more reliable machine. But the underlying reasons could be more complex. They might need the laptop to handle resource-intensive tasks like video editing or 3D rendering, or they might want a device that can seamlessly switch between work and personal use.
Step 2: Define the Success Criteria
Once the job is identified, the next step is to define what success looks like for the consumer. This involves setting clear and measurable goals. For example, if the job is to improve productivity, success criteria could include increased speed of task completion, reduced errors, or enhanced collaboration capabilities.
Step 3: Understand the Customer’s Current Approach
Understanding how the customer is currently trying to get the job done is crucial. This step involves analyzing their existing methods, tools, and processes. Are they using a combination of different tools? Are there any workarounds or temporary solutions they’ve implemented? By understanding the current state, businesses can identify pain points and areas for improvement.
Step 4: Identify the Gaps and Opportunities
This step involves comparing the current state with the desired success criteria. By identifying the gaps between the two, businesses can uncover opportunities for innovation. These gaps could be in terms of functionality, user experience, or even the overall value proposition of the product or service.
For example, if the customer is currently using a slow and unreliable laptop for video editing, the gap could be in terms of processing power and speed. An opportunity might arise in the form of a high-performance laptop with advanced graphics capabilities, tailored specifically for video editors.
Step 5: Develop Solutions
With a clear understanding of the job, success criteria, and gaps, businesses can now develop solutions that address these needs. This step involves creativity, innovation, and a deep understanding of the target audience. The solutions could range from developing new products or services to enhancing existing offerings.
In the case of the video editor, the solution could be a laptop with powerful processing capabilities, a high-resolution display for precise editing, and advanced software integration for seamless workflow.
The Benefits of the JTBD Framework
The JTBD framework offers a multitude of benefits to businesses, helping them stay ahead of the competition and deliver products and services that truly meet customer needs:
- Enhanced Customer Understanding: By focusing on the customer's job, businesses gain a deeper understanding of their motivations, pain points, and aspirations. This enables them to develop solutions that are more relevant and valuable to the target audience.
- Innovative Product Development: The JTBD framework encourages businesses to think beyond existing solutions and explore new possibilities. By identifying gaps and opportunities, businesses can develop innovative products and services that truly differentiate themselves in the market.
- Improved Market Positioning: With a clear understanding of the customer's job, businesses can position their products and services more effectively. They can communicate the value proposition in a way that resonates with the target audience, making it easier to attract and retain customers.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: By delivering solutions that meet or exceed customer expectations, businesses can foster higher levels of satisfaction and loyalty. Customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates when their specific needs are addressed.
- Reduced Market Risk: The JTBD framework helps businesses reduce market risk by ensuring that their products and services are aligned with customer needs. By understanding the job, businesses can develop solutions that have a higher likelihood of success and market acceptance.
Real-World Examples of JTBD in Action
The Jobs To Be Done framework has been successfully applied by numerous businesses across various industries, resulting in innovative products and services that have disrupted markets and captivated consumers.
Example 1: Airbnb
Airbnb, the popular online marketplace for lodging, successfully applied the JTBD framework to disrupt the traditional hospitality industry. The job that Airbnb identified was to provide travelers with unique, affordable, and flexible accommodation options.
By understanding the functional job (finding suitable lodging), emotional job (experiencing a sense of belonging and connection), and social job (interacting with locals and gaining insider knowledge), Airbnb developed a platform that revolutionized the way people travel. They offered a unique value proposition that appealed to both hosts and guests, resulting in a massive shift in the industry.
Example 2: Netflix
Netflix, the leading subscription-based streaming service, also utilized the JTBD framework to transform the way people consume entertainment. The job they identified was to provide viewers with convenient, personalized, and affordable access to a vast array of entertainment content.
By understanding the functional job (easy access to a wide range of shows and movies), emotional job (the joy of discovering new content and the comfort of rewatching favorites), and social job (sharing recommendations and discussions with friends), Netflix developed a platform that has become a staple in many households. Their innovative approach to content distribution and personalized recommendations has kept them at the forefront of the entertainment industry.
Example 3: Tesla
Tesla, the electric vehicle and clean energy company, has applied the JTBD framework to disrupt the automotive industry. The job they identified was to provide environmentally conscious consumers with high-performance, stylish, and sustainable transportation options.
By understanding the functional job (efficient and reliable transportation), emotional job (the thrill of driving a high-performance vehicle and contributing to a greener planet), and social job (making a statement about one's environmental values), Tesla developed electric vehicles that have captured the imagination of consumers worldwide. Their innovative approach to automotive design and technology has not only challenged traditional automakers but also paved the way for a more sustainable future.
The Future of the Jobs To Be Done Framework

The Jobs To Be Done framework is an evolving concept that continues to shape the way businesses approach product development and market strategy. As consumer needs and preferences continue to evolve, the framework provides a robust methodology for businesses to stay relevant and competitive.
With the rise of digital transformation and the increasing importance of customer experience, the JTBD framework is more relevant than ever. Businesses that embrace this approach are likely to gain a competitive edge by developing products and services that truly resonate with their target audience. By understanding the jobs that consumers are trying to accomplish, businesses can create solutions that not only meet but exceed expectations, leading to long-term success and growth.
In a rapidly changing business landscape, the JTBD framework provides a compass for businesses to navigate the complexities of the market and deliver exceptional value to their customers. As businesses continue to innovate and adapt, the Jobs To Be Done framework will undoubtedly remain a powerful tool for understanding and meeting consumer needs.
What is the key difference between the Jobs To Be Done framework and traditional market research methods?
+The Jobs To Be Done framework differs from traditional market research methods in its focus on understanding the “job” that consumers are trying to accomplish rather than solely relying on demographic data or customer feedback. While traditional methods provide valuable insights, the JTBD framework goes a step further by delving into the motivations, goals, and aspirations of consumers. This deeper understanding allows businesses to develop solutions that are more aligned with customer needs and expectations.
How can businesses use the JTBD framework to enhance their market positioning?
+By applying the JTBD framework, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their target audience’s needs and aspirations. This knowledge allows them to position their products or services in a way that resonates with customers. By clearly communicating how their offerings help customers get their jobs done, businesses can differentiate themselves in the market and attract the right audience.
What are some challenges businesses might face when implementing the JTBD framework?
+One of the main challenges is ensuring that the research and analysis are conducted thoroughly and accurately. The framework relies on in-depth customer understanding, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Additionally, businesses may need to adapt their existing processes and mindsets to fully embrace the JTBD approach. However, with the right tools, resources, and commitment, these challenges can be overcome.



