Jobs In The Federal Court System
Exploring Career Opportunities in the Federal Court System: A Comprehensive Guide

The federal court system in the United States is a dynamic and integral part of the nation's judicial landscape, offering a wide array of career opportunities for legal professionals and those passionate about the justice system. This guide delves into the diverse roles within the federal courts, shedding light on the qualifications, responsibilities, and potential career paths for individuals interested in pursuing a career in this esteemed branch of the legal field.
Understanding the Federal Court System

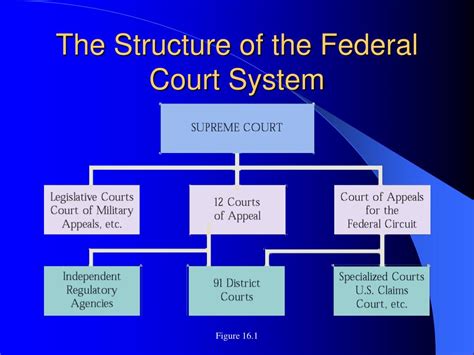
The federal court system is a hierarchical structure, comprising three levels: the Supreme Court, the Federal Appellate Courts (Circuit Courts), and the Federal District Courts. Each level plays a crucial role in the administration of justice, and the nature of work and career prospects varies significantly across these tiers.
Supreme Court
The Supreme Court stands at the pinnacle of the federal judiciary, acting as the highest court in the land. While career opportunities within the Supreme Court are limited, the roles are highly prestigious and influential. The Supreme Court typically hires law clerks to assist the justices in researching and drafting opinions. Law clerks are generally recent law school graduates who have demonstrated exceptional academic achievement and a deep understanding of the law. The competitive nature of these positions often requires a strong network of connections and a reputation for legal excellence.
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Law Clerk | Assists justices in legal research and opinion drafting |

Federal Appellate Courts (Circuit Courts)
Federal Appellate Courts, also known as Circuit Courts, serve as the intermediate appellate level in the federal judiciary. These courts review decisions made by the Federal District Courts and have jurisdiction over a specific geographic area, known as a circuit. Career opportunities in these courts include positions such as:
- Appellate Judge: Federal appellate judges preside over cases that have been appealed from the district courts. They review the legal issues and factual findings of the lower courts and issue written opinions. The appointment process for federal judges is highly political and often involves a rigorous confirmation process by the Senate.
- Law Clerk: Similar to the Supreme Court, law clerks in the Circuit Courts assist judges in researching and drafting opinions. These positions are highly competitive and often serve as a stepping stone for future legal careers.
- Staff Attorney: Staff attorneys provide legal support to the court, often working on specific projects or cases assigned by the judges. They may conduct legal research, draft memoranda, and assist in case management.
Federal District Courts
Federal District Courts are the trial courts of the federal judiciary, where cases are initially heard and decided. These courts have jurisdiction over a wide range of matters, including civil disputes, criminal cases, and administrative law issues. Career opportunities in the Federal District Courts are diverse and offer a range of legal specialties.
- District Judge: District judges preside over trials and make decisions on legal matters brought before the court. They issue rulings on motions, conduct jury trials, and determine the outcome of cases. The appointment process for district judges is similar to that of appellate judges, involving presidential nomination and Senate confirmation.
- Magistrate Judge: Magistrate judges assist district judges by conducting preliminary hearings, resolving pretrial matters, and presiding over misdemeanor trials. They also often handle settlement conferences and alternative dispute resolution processes.
- Courtroom Deputy: Courtroom deputies play a vital role in the smooth operation of the court. They manage the court's calendar, coordinate with litigants and attorneys, and ensure that the courtroom is prepared for each hearing or trial.
- Court Reporter: Court reporters are responsible for creating an accurate record of court proceedings. They transcribe everything that is said during a hearing or trial, ensuring a precise written record for future reference.
- Probation Officer: Probation officers work closely with the court, primarily in criminal cases. They conduct pre-sentence investigations, prepare reports for the judge, and supervise individuals on probation or parole.
Qualifications and Education
The qualifications for roles within the federal court system vary depending on the position and the level of the court. However, a strong foundation in legal education is typically a prerequisite for most careers in this field.
- Law Degree: A Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree from an accredited law school is often the minimum requirement for many positions, especially for judges and attorneys. Law school provides a comprehensive understanding of legal principles, research skills, and the practical application of law.
- Legal Experience: Many roles within the federal court system require practical legal experience. This can include working as an attorney in private practice, serving as a law clerk, or holding positions in government legal departments.
- Specialized Knowledge: Certain positions may require specialized knowledge or expertise in specific areas of law. For example, tax law, intellectual property, or environmental law may be advantageous for certain roles.
- Professional Reputation: Building a strong professional reputation is crucial for career advancement within the federal court system. This often involves demonstrating excellence in legal practice, maintaining a high level of ethics, and contributing to the legal community through publications or speaking engagements.
Career Pathways and Growth
The federal court system offers a range of career pathways, each with its own trajectory for growth and advancement. While some roles, such as law clerks and courtroom deputies, may be entry-level positions, they often serve as stepping stones to more senior roles within the judiciary or legal profession.
- Judicial Career Path: For those interested in a career as a judge, the federal court system provides a clear pathway. Starting as a law clerk or attorney, individuals can gain experience and build a reputation that may lead to judicial appointments. Judges often progress through the ranks, moving from district courts to appellate courts and, in exceptional cases, to the Supreme Court.
- Legal Practice: Many individuals who work within the federal court system, such as staff attorneys or probation officers, often have the opportunity to transition into private legal practice. The skills and experience gained within the court system can be valuable assets in a law firm or corporate legal department.
- Government Legal Roles: The federal court system is closely intertwined with other branches of the government, including the Department of Justice and various regulatory agencies. Career paths within these government entities often involve working closely with the federal courts, providing another avenue for legal professionals to explore.
Conclusion

The federal court system offers a wealth of career opportunities for individuals passionate about the law and the administration of justice. From the esteemed role of a Supreme Court justice to the vital support roles within the district courts, each position plays a crucial part in ensuring a fair and efficient judicial process. With a strong foundation in legal education and a commitment to excellence, individuals can forge successful and rewarding careers within this dynamic and influential branch of the legal field.
What are the main types of cases heard in Federal District Courts?
+Federal District Courts handle a wide range of cases, including civil disputes between citizens of different states, cases involving the constitutionality of federal laws, criminal cases involving federal crimes, and cases related to administrative law, such as challenges to agency decisions.
How are federal judges appointed, and what is the confirmation process like?
+Federal judges, both district and appellate, are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate. The process involves a thorough background check, a hearing before the Senate Judiciary Committee, and a vote by the full Senate. The confirmation process can be highly political and often involves extensive scrutiny of the nominee’s legal record and personal beliefs.
What are the key differences between a law clerk position at the Supreme Court and Circuit Courts?
+While both Supreme Court and Circuit Court law clerks assist judges in researching and drafting opinions, the roles differ in scope and impact. Supreme Court law clerks work directly with the justices on cases that have significant impact on national law and policy. Circuit Court law clerks, while also important, work within a more regional context and often have a greater focus on practical application of the law.



