Jobs In Supply Chain Management

The field of supply chain management (SCM) is a vital aspect of modern business operations, encompassing the entire journey of a product or service from its inception to delivery to the end customer. With a focus on optimizing processes, reducing costs, and ensuring timely and efficient delivery, SCM professionals play a crucial role in today's globalized and competitive marketplace.
This article delves into the diverse and dynamic world of jobs in supply chain management, exploring the various roles, their responsibilities, and the skills required to succeed in this exciting and ever-evolving field. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the career opportunities within SCM and the steps you can take to forge a successful path in this rewarding industry.
The Diverse Roles in Supply Chain Management

Supply chain management is a multifaceted discipline, and as such, it offers a wide array of specialized roles and career paths. Each role contributes uniquely to the smooth functioning of the supply chain, from procurement and logistics to inventory management and quality control. Here’s an overview of some of the key positions within the SCM landscape:
Supply Chain Manager
At the heart of any successful supply chain operation is the supply chain manager. This role demands a broad understanding of the entire supply chain process, from initial procurement to final delivery. Supply chain managers are responsible for strategic planning, resource allocation, and ensuring that the supply chain operates efficiently and cost-effectively. They must be adept at negotiating with suppliers, managing inventory levels, and overseeing logistics to meet customer demands.
Supply chain managers often work closely with other departments, such as marketing and finance, to align supply chain strategies with overall business goals. They are also responsible for identifying areas of improvement, implementing new processes, and staying abreast of industry trends and technologies.
Logistics Coordinator
Logistics coordinators are the orchestrators of the physical movement of goods within the supply chain. They are responsible for planning, implementing, and managing the efficient, effective flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This involves coordinating with various transportation modes, such as air, sea, road, and rail, to ensure timely and safe delivery.
Logistics coordinators also manage warehousing and distribution centers, ensuring optimal inventory levels and efficient order fulfillment. They must be adept at using logistics software and technologies to track and trace shipments, manage delivery schedules, and handle any disruptions or delays in the supply chain.
Procurement Specialist
Procurement specialists, often referred to as purchasing agents, play a critical role in the supply chain by identifying and acquiring the goods and services needed by their organization. They source suppliers, negotiate contracts, and manage the purchasing process to ensure that the organization receives the best possible value for its money.
Procurement specialists must have excellent negotiation skills, a keen eye for detail, and the ability to analyze and compare suppliers based on factors such as cost, quality, reliability, and sustainability. They often work closely with other departments to understand their specific needs and requirements and to ensure that the organization's purchasing policies are followed.
Inventory Manager
Inventory managers are responsible for overseeing the organization’s stock of goods, ensuring that the right products are available in the right quantities at the right time. They must balance the need to maintain sufficient inventory levels to meet customer demands with the desire to minimize costs associated with excess stock.
Inventory managers use a variety of tools and techniques, such as inventory management software, just-in-time inventory systems, and statistical forecasting, to optimize inventory levels. They must also be adept at analyzing inventory data, identifying trends, and making informed decisions to improve inventory turnover and reduce costs.
Quality Assurance Manager
Quality assurance managers are vital to the supply chain as they ensure that the goods and services delivered meet the required standards of quality, safety, and reliability. They develop and implement quality control processes, oversee testing and inspection procedures, and work closely with suppliers to maintain high standards throughout the supply chain.
Quality assurance managers must have a deep understanding of quality management principles and techniques, as well as strong leadership and communication skills to effectively manage quality assurance teams and collaborate with other departments. They play a critical role in maintaining customer satisfaction and building the organization's reputation for delivering high-quality products and services.
Skills and Qualifications for Success in SCM
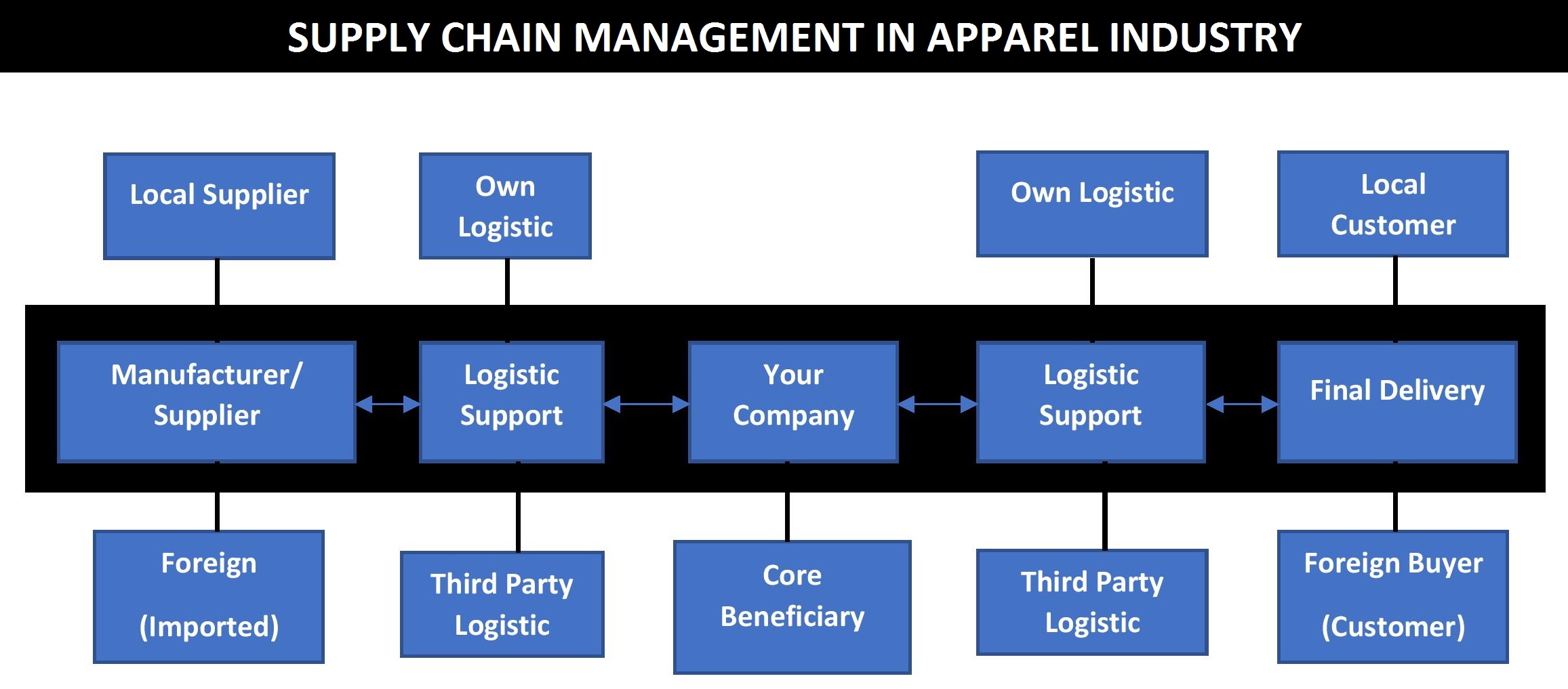
Given the diverse nature of supply chain management roles, a broad range of skills and qualifications are required to succeed in this field. While specific skills may vary depending on the role, there are several core competencies that are highly valued across the SCM landscape:
- Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze data, identify trends, and make informed decisions is crucial in supply chain management. Professionals must be able to interpret data from various sources, such as sales reports, inventory levels, and transportation costs, to optimize supply chain processes.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Supply chain managers often face complex challenges, from managing disruptions in the supply chain to resolving conflicts between departments. Strong problem-solving skills are essential to identify root causes, develop effective solutions, and implement them successfully.
- Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration are key to building strong relationships with internal teams, suppliers, and customers. SCM professionals must be able to communicate complex supply chain concepts clearly and concisely to stakeholders with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Negotiation and Persuasion: Negotiation skills are vital for SCM roles, particularly in procurement and logistics. Professionals must be adept at negotiating contracts, resolving disputes, and persuading stakeholders to adopt new processes or strategies.
- Attention to Detail: With the many moving parts in the supply chain, attention to detail is critical. SCM professionals must be able to spot potential issues, ensure accuracy in documentation and data entry, and maintain high standards of quality and safety.
- Leadership and Management: Leadership and management skills are essential for supply chain managers and quality assurance managers. These professionals must be able to lead and motivate teams, delegate tasks effectively, and make strategic decisions that align with the organization's goals.
In addition to these core competencies, many SCM roles also require specialized knowledge and skills. For example, logistics coordinators may need to be proficient in logistics software and transportation management systems, while procurement specialists may require expertise in contract law and supplier relationship management.
The Impact of Technology on SCM Careers
Technology has been a game-changer in supply chain management, revolutionizing the way goods and services are procured, transported, and delivered. The increasing adoption of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT), has led to significant changes in the skills and qualifications required for SCM professionals.
One of the most significant impacts of technology on SCM careers is the need for digital literacy and data analytics skills. With the vast amounts of data generated by supply chain processes, professionals must be able to collect, analyze, and interpret data to make informed decisions. This requires proficiency in data analytics tools and techniques, as well as an understanding of how to leverage technology to optimize supply chain operations.
Furthermore, the integration of AI and ML in SCM has led to the development of intelligent systems that can automate repetitive tasks, optimize inventory levels, and predict supply chain disruptions. SCM professionals must be comfortable working with these technologies and have the skills to leverage them effectively. This includes an understanding of how to train and deploy AI models, as well as how to interpret and act upon the insights generated by these systems.
The IoT has also had a significant impact on SCM careers, particularly in logistics and transportation. The ability to track and monitor shipments in real-time, as well as collect and analyze data from sensors embedded in products and vehicles, has revolutionized the way goods are moved and managed. SCM professionals must be able to utilize IoT technologies to enhance visibility and efficiency in the supply chain.
Education and Training for SCM Careers
While a solid educational foundation is essential for a career in supply chain management, the field is highly dynamic and requires continuous learning and skill development. A bachelor’s degree in supply chain management, logistics, or a related field is often the minimum requirement for entry-level positions. However, many employers prefer candidates with advanced degrees, such as a Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a concentration in supply chain management or a Master of Science in Logistics or Supply Chain Management.
In addition to formal education, professional certifications can enhance the credentials of SCM professionals and open up new career opportunities. Some of the most recognized certifications in the field include the Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP) offered by the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), the Certified Professional in Supply Management (CPSM) offered by the Institute for Supply Management (ISM), and the Certified in Production and Inventory Management (CPIM) offered by ASCM.
Ongoing training and professional development are also crucial for SCM professionals to stay abreast of industry trends, technological advancements, and best practices. Many employers offer internal training programs to help their employees stay current, while external training courses and conferences provide opportunities to network and learn from industry experts.
Future Outlook for SCM Careers

The future of supply chain management careers is bright, with strong demand for skilled professionals across a wide range of industries. As businesses continue to globalize and competition intensifies, the efficient and effective management of supply chains becomes even more critical. This, coupled with the increasing complexity of supply chains and the rapid pace of technological change, creates a wealth of opportunities for those with the right skills and qualifications.
One of the most significant trends shaping the future of SCM careers is the continued integration of technology into supply chain processes. The use of AI, ML, and IoT is expected to grow, leading to the development of more intelligent and efficient supply chain systems. Professionals with expertise in these technologies will be in high demand, particularly those who can combine technical skills with a deep understanding of supply chain processes and business needs.
Sustainability and environmental concerns are also expected to play an increasingly important role in SCM careers. As businesses strive to reduce their environmental impact and meet sustainability goals, SCM professionals will need to develop strategies and processes that minimize waste, optimize energy use, and promote responsible sourcing and production practices. This will require a combination of technical expertise, business acumen, and a commitment to environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Supply chain management offers a diverse range of exciting career opportunities, from supply chain managers and logistics coordinators to procurement specialists and quality assurance managers. With the right skills, qualifications, and a commitment to continuous learning, professionals can forge successful and rewarding careers in this dynamic and critical field. As the world of business becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the role of SCM professionals in driving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring timely delivery of goods and services will only grow in importance.
By staying abreast of industry trends, leveraging technology effectively, and embracing sustainable practices, SCM professionals can position themselves at the forefront of this rapidly evolving industry. The future of supply chain management is bright, and those who embrace its challenges and opportunities will undoubtedly thrive in their careers.
What are the key skills required for a career in supply chain management?
+Supply chain management professionals require a range of skills, including analytical abilities, problem-solving skills, effective communication, negotiation expertise, attention to detail, and leadership qualities. Additionally, with the increasing role of technology, digital literacy and data analytics skills are becoming increasingly important.
How can I prepare for a career in supply chain management?
+Preparing for a career in supply chain management involves obtaining a relevant degree, such as in supply chain management, logistics, or business administration, and considering professional certifications like the CSCP, CPSM, or CPIM. Continuous learning and staying updated with industry trends and technologies are also crucial.
What are some of the challenges faced by supply chain managers?
+Supply chain managers often face challenges such as managing disruptions in the supply chain, negotiating with suppliers and stakeholders, optimizing inventory levels, ensuring quality and safety standards, and staying abreast of technological advancements and industry trends.
How is technology impacting careers in supply chain management?
+Technology is revolutionizing supply chain management careers by introducing new skills requirements, such as digital literacy and data analytics. The integration of AI, ML, and IoT is expected to continue, leading to more efficient and intelligent supply chain systems. Professionals with expertise in these technologies will be in high demand.
What is the future outlook for supply chain management careers?
+The future of supply chain management careers looks promising, with strong demand for skilled professionals. The continued integration of technology, the focus on sustainability, and the increasing complexity of supply chains present exciting opportunities for those with the right skills and qualifications.



