Job Cost Accounting

Job Cost Accounting is a crucial aspect of business management, particularly in industries where projects and contracts are the primary sources of revenue. This method of accounting allows businesses to track the costs associated with specific jobs or projects, providing valuable insights into profitability and helping organizations make informed decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Job Cost Accounting, exploring its definition, key components, benefits, and real-world applications. By the end, you'll have a deep understanding of how this accounting practice can enhance your business's financial management and overall success.
Understanding Job Cost Accounting
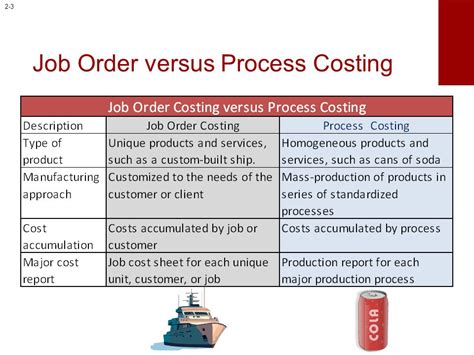
Job Cost Accounting, often referred to as Project Cost Accounting, is a specialized branch of cost accounting tailored to businesses that operate on a project-by-project basis. It involves a meticulous process of recording, analyzing, and allocating costs to individual jobs or projects. This accounting method provides a clear financial picture of each project, helping businesses understand their financial performance and make strategic decisions.
Unlike traditional accounting methods that focus on a company's overall financial health, Job Cost Accounting zeros in on the specific costs and revenues associated with individual projects. This level of detail is essential for businesses in sectors like construction, engineering, consulting, and manufacturing, where projects vary widely in scope and duration.
Key Components of Job Cost Accounting
Job Cost Accounting comprises several crucial elements that work together to provide a comprehensive financial overview of projects. These components include:
- Job Costing: The core of Job Cost Accounting, this process involves allocating costs directly to individual jobs or projects. Costs can include direct materials, direct labor, and overhead expenses. Job costing ensures that each project's financial impact is accurately captured.
- Direct Costs: These are the expenses that can be directly attributed to a specific project. Examples include raw materials, labor wages, and subcontractor fees. Direct costs are often the most significant component of a project's total cost.
- Indirect Costs: Also known as overhead costs, these are expenses that cannot be directly tied to a single project. Examples include office rent, insurance, and administrative salaries. Indirect costs are allocated to projects based on predetermined allocation rates.
- Cost Accumulation: This process involves collecting and organizing cost data from various sources, such as purchase orders, timesheets, and expense reports. Accurate cost accumulation is vital for ensuring the integrity of financial records.
- Cost Allocation: Once costs are accumulated, they need to be allocated to the appropriate projects. Cost allocation methods can vary, but common approaches include direct costing, activity-based costing, and percentage-of-completion methods.
Benefits of Job Cost Accounting

Implementing Job Cost Accounting offers a range of advantages to businesses, particularly those operating in project-based industries. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced Financial Control
Job Cost Accounting provides a detailed financial breakdown of each project, allowing businesses to exercise better control over their finances. By understanding the exact costs associated with each job, companies can make more informed decisions about pricing, budgeting, and resource allocation.
Improved Profitability Analysis
With Job Cost Accounting, businesses can analyze the profitability of individual projects. This level of analysis helps identify profitable and unprofitable projects, allowing for strategic adjustments to improve overall profitability. It also aids in setting competitive pricing strategies.
Better Resource Allocation
By tracking costs at the project level, businesses can optimize their resource allocation. They can identify which projects require more resources, which projects are overperforming, and which resources are being underutilized. This information enables efficient allocation of staff, materials, and equipment.
Accurate Billing and Invoicing
Job Cost Accounting ensures that billing and invoicing processes are accurate and timely. With detailed cost records, businesses can create invoices that reflect the true costs of each project, minimizing the risk of undercharging or overcharging clients.
Risk Management
This accounting method helps identify potential risks associated with projects. By analyzing cost trends and comparing actual costs to budgeted costs, businesses can anticipate and mitigate financial risks, ensuring project success and client satisfaction.
Real-World Applications of Job Cost Accounting
Job Cost Accounting is particularly relevant and beneficial in several industries. Let’s explore some real-world examples of how this accounting method is applied:
Construction Industry
In the construction industry, Job Cost Accounting is crucial for managing the costs of individual construction projects. From residential homes to commercial buildings, each project has unique requirements and cost structures. By using Job Cost Accounting, construction companies can track material costs, labor expenses, and overhead, ensuring accurate billing and profitability analysis.
Engineering Firms
Engineering firms often work on a variety of projects, from designing bridges to developing software. Job Cost Accounting helps these firms allocate costs to specific projects, whether it’s a large-scale infrastructure project or a smaller software development task. This ensures that each project’s financial impact is accurately reflected.
Consulting Services
Consulting firms, whether they specialize in management consulting, IT consulting, or legal consulting, often bill their clients based on the hours worked and expenses incurred. Job Cost Accounting allows consulting firms to track these hours and expenses accurately, ensuring fair billing and helping them manage their profitability.
Manufacturing Enterprises
Manufacturing businesses often produce a wide range of products, each with its own unique cost structure. Job Cost Accounting enables these enterprises to allocate costs to specific products or production runs, providing insights into the profitability of each product line and helping with pricing decisions.
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
Job Cost Accounting is not just about tracking costs; it’s also a powerful tool for performance analysis and strategic decision-making. By analyzing cost data over time, businesses can identify trends, evaluate the efficiency of their operations, and make data-driven decisions to improve performance.
For example, a construction company might use Job Cost Accounting to compare the costs of similar projects over the years. This analysis can reveal trends in material prices, labor rates, or project overruns, helping the company adjust its bidding strategies and improve project management practices.
Moreover, Job Cost Accounting can inform strategic planning and business development. By understanding the profitability of different types of projects, businesses can focus on the most lucrative projects, diversify their offerings, or identify areas for cost reduction.
Technological Advances in Job Cost Accounting
With the advancement of technology, Job Cost Accounting has become more efficient and accurate. Cloud-based accounting software and mobile applications have made it easier for businesses to track costs in real-time, ensuring that financial data is always up-to-date. Additionally, these technologies often provide robust reporting and analytics tools, making performance analysis more accessible and actionable.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, Job Cost Accounting is expected to continue evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. As industries become more data-driven and competitive, the demand for accurate and timely financial information will only increase. This may lead to further integration of Job Cost Accounting with other business systems, such as project management software and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to create a seamless flow of data across the organization.
Furthermore, with the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning, Job Cost Accounting may see the development of predictive analytics tools. These tools could forecast project costs and profitability, helping businesses make even more informed decisions and improve their financial performance.
What are the key differences between Job Cost Accounting and traditional accounting methods?
+Job Cost Accounting differs from traditional accounting methods in its focus on individual projects or jobs. While traditional accounting provides a company-wide financial overview, Job Cost Accounting offers a detailed breakdown of costs and revenues for each project. This level of detail is crucial for businesses operating in project-based industries.
How does Job Cost Accounting help with budgeting and forecasting?
+Job Cost Accounting provides accurate cost data for individual projects, which is essential for budgeting and forecasting. By understanding the actual costs associated with past projects, businesses can create more realistic budgets for future projects and make better financial forecasts. This helps prevent underestimating costs and ensures better financial planning.
Can Job Cost Accounting be applied to small businesses?
+Absolutely! Job Cost Accounting is beneficial for businesses of all sizes, especially those operating in project-based industries. Small businesses can use this method to gain better control over their finances, improve profitability, and make informed decisions about their projects. Modern accounting software often offers user-friendly solutions tailored to small businesses.



