Grey Collar Jobs
In the ever-evolving landscape of the modern workforce, a new term has emerged: "grey collar jobs." This term, though relatively new, encapsulates a significant portion of the job market, bridging the gap between traditional blue-collar and white-collar roles. But what exactly are grey collar jobs, and why are they gaining prominence in today's economic discourse? Let's delve into this fascinating segment of the professional world.
Understanding Grey Collar Jobs
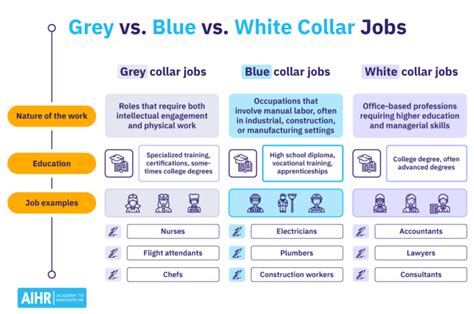
Grey collar jobs are a category of employment that blends aspects of both blue-collar and white-collar work. These roles typically involve skilled labor, often requiring a combination of technical expertise, manual skills, and intellectual capabilities. Unlike their blue-collar counterparts, who are predominantly engaged in physical labor, and white-collar workers, who primarily work in offices, grey collar professionals often find themselves in unique environments that demand a diverse skill set.
The term "grey collar" suggests a middle ground, where individuals are not purely manual laborers or office-bound professionals. Instead, they navigate a space where knowledge, skills, and experience are valued equally. These jobs often require a higher level of education or training compared to traditional blue-collar roles, yet they may not always necessitate a university degree, making them accessible to a broader range of individuals.
One of the key characteristics of grey collar jobs is their focus on technical skills. These roles often involve the application of specialized knowledge, whether it's in manufacturing, healthcare, information technology, or other sectors. The workers in these fields are highly skilled, and their expertise is crucial to the smooth operation of various industries.
Examples of Grey Collar Jobs

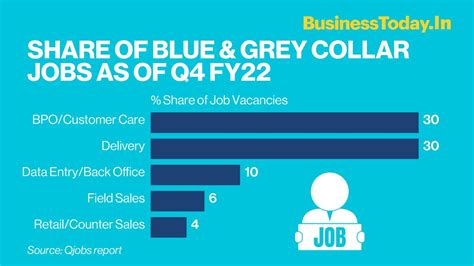
Grey collar jobs encompass a wide range of professions, each with its unique set of skills and requirements. Here are some examples that illustrate the diversity within this category:
1. IT Technicians
Information Technology (IT) technicians are a prime example of grey collar workers. These professionals possess a blend of technical knowledge and practical skills. They are responsible for installing, maintaining, and repairing computer systems and networks. While they often work in an office environment, their role requires a significant amount of hands-on work, troubleshooting technical issues, and providing on-site support.
2. Healthcare Technologists
The healthcare industry is another sector that boasts a significant number of grey collar jobs. Healthcare technologists, such as radiologic technologists, medical laboratory technologists, and respiratory therapists, combine their understanding of medical sciences with practical skills to operate complex medical equipment. These professionals play a vital role in patient care, often working alongside doctors and nurses.
3. Manufacturing Supervisors
In the manufacturing sector, grey collar jobs are prevalent. Manufacturing supervisors, for instance, oversee production processes, manage teams, and ensure quality control. They require a deep understanding of the manufacturing process, as well as leadership and organizational skills. These professionals often bridge the gap between the factory floor and upper management.
4. Renewable Energy Technicians
With the growing focus on sustainable energy, renewable energy technicians have emerged as a key grey collar profession. These technicians install, maintain, and repair solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems. Their work involves a combination of technical knowledge, practical skills, and an understanding of environmental sciences.
5. Aviation Maintenance Technicians
Aviation maintenance technicians are crucial to the safe operation of aircraft. These professionals inspect, repair, and maintain airplanes and helicopters. Their role requires a high level of technical expertise, as well as attention to detail and adherence to strict safety protocols. Aviation maintenance is a prime example of a grey collar job that demands both practical skills and theoretical knowledge.
The Benefits and Challenges of Grey Collar Jobs
Grey collar jobs offer a unique set of advantages and challenges for both employers and employees. For employers, these roles provide a skilled workforce that can adapt to the changing demands of the industry. Grey collar workers are often versatile, capable of taking on various responsibilities, and they bring a wealth of practical experience to the table.
From an employee's perspective, grey collar jobs can be highly rewarding. These roles often provide a sense of purpose and satisfaction that comes with applying one's skills and knowledge directly to a task. Grey collar workers are in high demand, and their expertise is valued across various industries. Additionally, these jobs can offer a good work-life balance, as they typically require less formal education than some white-collar roles.
However, there are also challenges associated with grey collar jobs. The demand for continuous learning and skill development is high, as technologies and processes evolve rapidly. Additionally, the physical nature of some grey collar roles can lead to health and safety concerns, requiring employers to implement robust health and safety measures.
The Future of Grey Collar Jobs
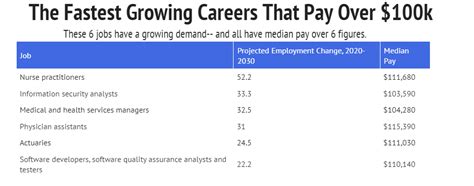
As industries continue to evolve and technology advances, the demand for grey collar workers is expected to grow. The unique skill set that grey collar professionals bring to the table makes them invaluable assets in a rapidly changing economic landscape. With the right support and training, these workers can adapt to new technologies and contribute to the growth and development of various sectors.
Furthermore, the rise of grey collar jobs highlights the importance of vocational and technical education. Many of these roles require specialized training, and initiatives to promote and enhance these educational pathways can help address skill gaps and ensure a competent workforce.
Conclusion

In a world where the lines between blue-collar and white-collar jobs are blurring, grey collar jobs offer a refreshing perspective on the modern workforce. These roles showcase the versatility and adaptability of today’s professionals, combining intellectual capabilities with practical skills. As we navigate the complexities of the modern economy, the grey collar worker will undoubtedly play a crucial role, driving innovation and progress across industries.
What distinguishes grey collar jobs from blue-collar and white-collar jobs?
+Grey collar jobs differ from blue-collar and white-collar jobs in their blend of skills and work environments. While blue-collar jobs primarily focus on physical labor, and white-collar jobs are office-based and often require a university degree, grey collar jobs require a combination of technical expertise, manual skills, and intellectual capabilities. Grey collar workers navigate a space that demands a diverse skill set, making them adaptable and versatile professionals.
What are some common challenges faced by grey collar workers?
+Grey collar workers often face the challenge of continuous learning and skill development due to the rapidly evolving nature of technology and processes. Additionally, the physical demands of some grey collar roles can lead to health and safety concerns, requiring careful management and adherence to protocols.
How can employers support and retain grey collar workers?
+Employers can support grey collar workers by investing in their professional development, offering training opportunities, and creating a culture that values their skills and contributions. Ensuring fair compensation and providing a safe and healthy work environment are also crucial aspects of retaining skilled grey collar professionals.