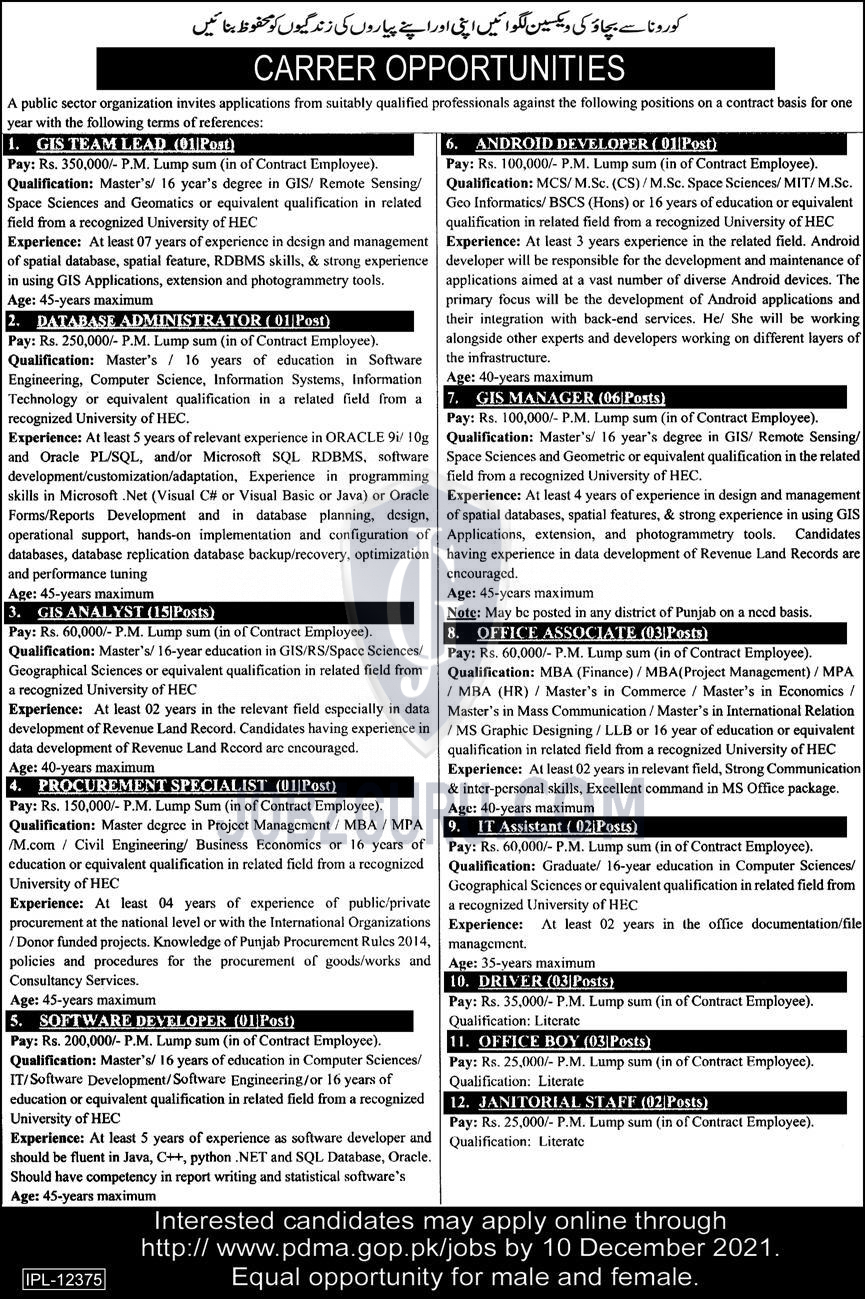
Gis Analyst Jobs
The field of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has seen tremendous growth and development in recent years, and with it, a surge in career opportunities for GIS analysts. GIS analysts play a crucial role in various industries, utilizing their expertise in mapping, data analysis, and spatial technologies to provide valuable insights and solutions. In this article, we will delve into the world of GIS analyst jobs, exploring the skills, responsibilities, and opportunities available in this exciting and dynamic field.
Understanding the Role of a GIS Analyst

A GIS analyst is a professional who specializes in the application of GIS technology to solve complex problems and make informed decisions. They are skilled in utilizing geographic data, spatial analysis techniques, and advanced software tools to visualize, analyze, and interpret geographical information. GIS analysts are in high demand across a wide range of sectors, including government, urban planning, environmental management, transportation, and many more.
The role of a GIS analyst involves a diverse set of responsibilities, including data collection, management, and processing. They work with various types of data, such as satellite imagery, GPS coordinates, survey data, and demographic information, to create comprehensive spatial databases. GIS analysts are experts in data visualization, creating maps, charts, and other visual representations to communicate complex spatial information effectively.
Key Skills and Qualifications for GIS Analyst Jobs

To excel as a GIS analyst, a strong foundation in GIS principles and technologies is essential. Here are some key skills and qualifications that employers often seek in GIS analyst candidates:
Technical Proficiency
- Proficiency in GIS software: Familiarity with industry-standard GIS software such as ESRI ArcGIS, QGIS, and ERDAS Imagine is crucial. GIS analysts should be skilled in data manipulation, analysis, and visualization using these tools.
- Database management: GIS analysts should have experience working with spatial databases, such as PostgreSQL with PostGIS or Microsoft SQL Server with Spatial capabilities. Knowledge of database query languages like SQL is highly advantageous.
- Remote sensing and imagery analysis: Understanding remote sensing principles and the ability to interpret and analyze satellite and aerial imagery are valuable skills for GIS analysts.
- GIS programming: Proficiency in programming languages commonly used in GIS, such as Python, R, or JavaScript, can set analysts apart. These skills enable them to automate tasks, develop custom tools, and integrate GIS with other technologies.
Analytical and Problem-Solving Abilities
GIS analysts must possess strong analytical skills to interpret spatial data and extract meaningful insights. They should be able to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data and use their expertise to solve complex geographical problems.
Cartographic Design and Visualization
Creating visually appealing and informative maps is an essential aspect of a GIS analyst’s work. Proficiency in cartographic principles, including map design, color theory, and symbology, is highly valued. GIS analysts should be able to communicate complex spatial information effectively through well-designed maps and visualizations.
Communication and Collaboration
GIS analysts often work as part of a team, collaborating with professionals from diverse backgrounds. Effective communication skills are vital to convey technical information to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. The ability to translate complex spatial concepts into accessible language is highly regarded.
GIS Analyst Job Opportunities
The demand for GIS analysts is growing across numerous industries, offering a wide range of career paths and opportunities. Let’s explore some of the key sectors that actively seek GIS analyst talent:
Government and Public Sector
Government agencies and public sector organizations heavily rely on GIS technology for various purposes. GIS analysts in this sector contribute to urban planning, land management, emergency response, and public health initiatives. They play a crucial role in decision-making processes, policy development, and the efficient delivery of public services.
Environmental Management and Conservation
GIS analysts are instrumental in environmental conservation and management efforts. They assist in monitoring and analyzing natural resources, tracking wildlife populations, and assessing the impact of human activities on ecosystems. GIS analysts in this field help organizations make informed decisions to protect and preserve the environment.
Transportation and Infrastructure Planning
The transportation industry heavily utilizes GIS technology for route planning, traffic analysis, and infrastructure development. GIS analysts in this sector contribute to optimizing transportation networks, analyzing traffic patterns, and identifying potential bottlenecks. They play a vital role in ensuring efficient and sustainable transportation systems.
Real Estate and Urban Development
GIS analysts are in high demand in the real estate and urban development industries. They assist in site selection, market analysis, and property valuation by leveraging spatial data and advanced GIS techniques. GIS analysts help developers and investors make informed decisions, ensuring successful and sustainable urban projects.
Energy and Utilities
The energy sector, including renewable energy projects, relies on GIS analysts for spatial analysis and planning. GIS analysts in this field contribute to optimizing energy infrastructure, analyzing renewable energy potential, and managing utility networks. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
GIS analyst jobs offer excellent career growth prospects, with opportunities for advancement and specialization. As analysts gain experience and expertise, they can explore various paths within the field, such as:
- Senior GIS Analyst: With experience, analysts can progress to senior roles, taking on more complex projects and providing leadership and guidance to junior team members.
- GIS Project Manager: Analysts with strong organizational and management skills can transition into project management roles, overseeing GIS projects from inception to completion.
- GIS Specialist: Analysts can specialize in specific domains, such as environmental GIS, transportation GIS, or health GIS, becoming experts in their chosen field.
- GIS Instructor or Educator: Experienced analysts with a passion for teaching can pursue careers in academia, sharing their knowledge and skills with the next generation of GIS professionals.
Conclusion

GIS analyst jobs offer a rewarding and dynamic career path for individuals with a passion for geography, technology, and problem-solving. With their unique skill set and expertise, GIS analysts play a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving informed decision-making across various industries. As GIS technology continues to evolve and advance, the demand for skilled GIS analysts will only continue to grow, opening up a world of exciting opportunities.
FAQ
What are the educational requirements for becoming a GIS analyst?
+A bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as geography, environmental science, or computer science, is typically required. However, some employers may prefer candidates with advanced degrees, such as a master’s or PhD, especially for specialized roles or research positions.
How can I gain practical experience as a GIS analyst?
+Practical experience is crucial for GIS analysts. Pursuing internships or volunteer opportunities with GIS-focused organizations or government agencies can provide valuable hands-on experience. Additionally, working on personal GIS projects or participating in online GIS communities can enhance your skills and showcase your expertise.
What are some in-demand GIS analyst specializations?
+GIS analyst specializations are diverse and depend on industry needs. Some in-demand specializations include environmental GIS, transportation GIS, urban planning GIS, health GIS, and GIS for natural resource management. Staying updated with industry trends and acquiring specialized skills can enhance your career prospects.
How can I stay updated with the latest GIS technologies and trends?
+The GIS industry is rapidly evolving, so it’s essential to stay updated. Attending GIS conferences, workshops, and webinars can provide valuable insights into emerging technologies and industry developments. Engaging with GIS communities online, following industry blogs and forums, and participating in professional development programs can also help you stay informed.



