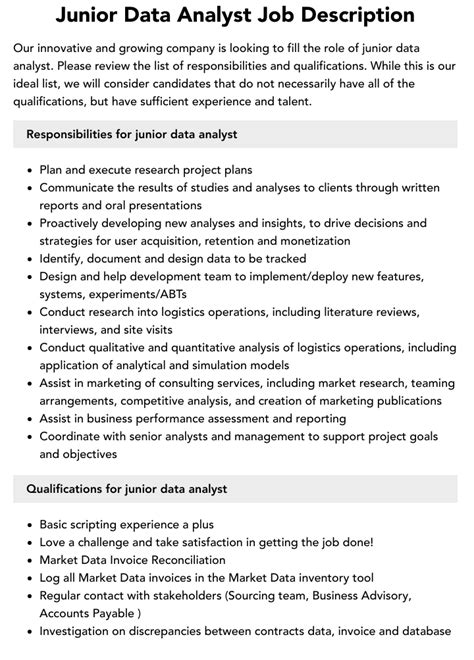
Database Analyst Job Description

The role of a Database Analyst is crucial in any organization that relies on data-driven decision-making. These professionals are the guardians of information, responsible for managing, analyzing, and interpreting vast datasets to provide valuable insights. In today's data-centric world, the demand for skilled Database Analysts is on the rise, making it an exciting and rewarding career path. This comprehensive guide will delve into the responsibilities, skills, and opportunities associated with the Database Analyst role, offering a detailed understanding of this vital profession.
Unveiling the Role of a Database Analyst

A Database Analyst serves as a bridge between complex data systems and business needs. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that data is not just stored efficiently but also retrieved, analyzed, and presented in a way that drives strategic decision-making. This involves a deep understanding of data structures, database management systems, and the ability to interpret and communicate complex information in a clear and actionable manner.
Key Responsibilities
- Designing and implementing database systems tailored to organizational needs.
- Ensuring data integrity and security through effective database management practices.
- Developing and maintaining database architectures that are scalable and efficient.
- Performing complex queries, data mining, and advanced analytics to extract meaningful insights.
- Collaborating with stakeholders to understand their data requirements and provide customized solutions.
- Documenting database structures, processes, and changes for future reference and maintenance.
Skills and Qualifications
To excel as a Database Analyst, a combination of technical prowess and analytical skills is essential. Here’s a breakdown of the key competencies:
- Technical Proficiency: Proficiency in database management systems such as SQL, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle is a must. Knowledge of NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra is an added advantage.
- Data Modeling and Design: The ability to design logical and physical data models that align with business requirements.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Skill in using analytical tools and techniques to extract meaningful patterns and trends from data.
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in programming languages like Python, R, or Java for data manipulation and script automation.
- Data Security and Privacy: A deep understanding of data protection regulations and best practices to ensure data confidentiality and integrity.
- Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication skills to convey complex technical concepts to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Analytical mindset to identify and resolve database-related issues efficiently.
The Impact of Database Analysts
The work of Database Analysts has a profound impact on the success and efficiency of organizations. Here’s how their contributions make a difference:
Data-Driven Decision Making
Database Analysts empower organizations to make informed decisions based on data. By providing accurate and timely insights, they enable businesses to optimize their strategies, identify new opportunities, and mitigate risks.
| Scenario | Impact of Database Analyst |
|---|---|
| Market Analysis | Identifying target demographics and market trends through data analysis. |
| Product Development | Analyzing customer feedback and market data to guide product improvements. |
| Risk Assessment | Predicting and mitigating potential risks based on historical data patterns. |

Efficient Data Management
Effective database management by analysts ensures that data is organized, accessible, and secure. This streamlines operations, reduces costs associated with data storage and retrieval, and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
Business Intelligence
Database Analysts play a pivotal role in generating actionable business intelligence. They translate complex data into digestible reports, dashboards, and visualizations, helping stakeholders make sense of the data and take appropriate actions.
Career Path and Opportunities
The field of database analysis offers a diverse range of career paths and opportunities. As a Database Analyst gains experience and deepens their expertise, they can explore various specializations and leadership roles.
Specializations
- Data Warehouse Analyst: Focuses on designing and maintaining data warehouses, a central repository for an organization’s data.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Converts raw data into actionable insights, often using visualization tools to present findings.
- Data Security Analyst: Specializes in protecting databases from unauthorized access and potential threats.
- Data Architect: Designs and develops data models and architectures to support organizational data needs.
Leadership Roles
- Database Administrator: Oversees the day-to-day management and maintenance of databases, ensuring optimal performance and security.
- Data Governance Manager: Leads data governance initiatives, ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and compliance with regulations.
- Chief Data Officer: Highest leadership position in data management, responsible for the overall data strategy and architecture of an organization.
The Future of Database Analysis
As technology advances and data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the role of Database Analysts will only become more critical. The field is expected to evolve with the integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain.
FAQs
What is the difference between a Database Analyst and a Data Analyst?
+
While both roles involve data analysis, Database Analysts focus specifically on managing and analyzing data within databases. Data Analysts, on the other hand, may work with various data sources and tools, including databases, spreadsheets, and statistical software.
What are the educational requirements for becoming a Database Analyst?
+
A bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field is typically required. However, relevant certifications and hands-on experience with database management systems can also be valuable.
How do Database Analysts ensure data security?
+
Database Analysts implement a range of security measures, including access controls, encryption, regular backups, and intrusion detection systems. They also stay updated with the latest security protocols and best practices.
What tools do Database Analysts commonly use?
+
Database Analysts utilize a variety of tools depending on their specific role and industry. Common tools include SQL databases, data visualization software like Tableau or Power BI, and programming languages such as Python or R.
How can Database Analysts stay updated with industry trends and advancements?
+
Attending industry conferences, participating in online communities and forums, and engaging in continuous learning through certifications and courses are effective ways for Database Analysts to stay updated with the latest trends and advancements.



