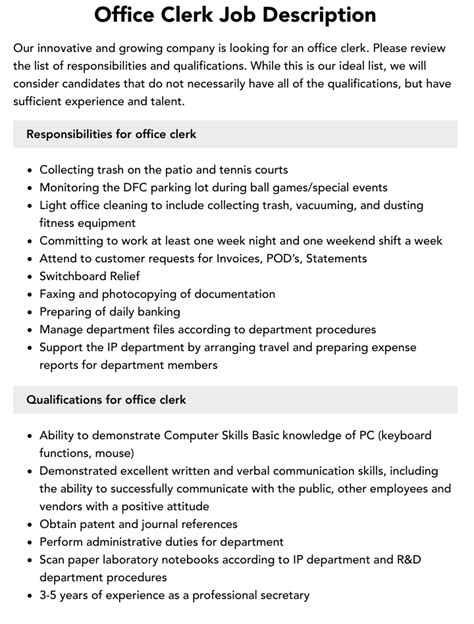
Clerk Job Description

A clerk is a vital role within various industries and organizations, responsible for performing essential administrative and support tasks that keep operations running smoothly. With a wide range of responsibilities, a clerk can be found in numerous sectors, from healthcare and finance to legal and retail, providing efficient assistance and contributing to the overall success of the business.
Duties and Responsibilities of a Clerk

The clerk’s role encompasses a diverse set of tasks, depending on the specific industry and workplace requirements. Here are some of the core duties and responsibilities associated with this position:
Administrative Support
Clerks are often the backbone of administrative operations. They handle various office management tasks, including organizing and maintaining records, drafting and distributing official correspondence, and coordinating meetings and events. Their efficiency in managing paperwork and digital documents ensures smooth workflow and communication within the organization.
Data Entry and Management
Data entry is a critical aspect of a clerk’s role. They input, update, and manage data across different systems, ensuring accuracy and confidentiality. From updating customer records to maintaining inventory databases, their meticulous data management skills contribute to the organization’s overall data integrity and security.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Database Maintenance | Regularly update and clean up databases to ensure data accuracy and accessibility. |
| Report Generation | Generate reports from collected data, providing valuable insights for decision-making. |
| Data Analysis | Analyze data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement within the organization. |

Customer Service and Communication
Interacting with customers and clients is another key aspect of a clerk’s role. They provide front-line support, answering inquiries, addressing concerns, and guiding customers through various processes. Effective communication skills and a customer-centric approach are essential to ensure a positive customer experience and build strong relationships.
Financial Transactions and Record-Keeping
In certain sectors, clerks handle financial transactions and record-keeping. This includes processing payments, managing invoices, and maintaining financial records. A keen eye for detail and accuracy is crucial to ensure financial transactions are handled securely and correctly.
Filing and Record Organization
Maintaining an organized filing system is a fundamental responsibility. Clerks create and manage physical and digital filing systems, ensuring easy access to important documents and records. Their organizational skills contribute to the efficiency of information retrieval and overall workplace productivity.
Qualifications and Skills
To excel as a clerk, a combination of educational qualifications and technical skills is required. Here’s an overview of the key qualifications and skills needed for this role:
Educational Requirements
A high school diploma or equivalent is typically the minimum educational requirement for a clerk position. However, many employers prefer candidates with some post-secondary education, such as an associate’s or bachelor’s degree in a related field like business administration, office management, or a specialized field depending on the industry.
Technical Skills
Proficiency in various software applications and technological tools is essential for a clerk. They should be well-versed in using office productivity software like Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), as well as email and calendar management systems. Additionally, knowledge of database management systems and basic data analytics tools can be advantageous.
Soft Skills
Beyond technical skills, clerks require a range of soft skills to excel in their role. Strong communication skills, both verbal and written, are vital for effective interaction with colleagues and customers. Organization and time management skills are crucial for handling multiple tasks and meeting deadlines. Clerks should also possess excellent problem-solving abilities and the ability to work independently and as part of a team.
Training and Professional Development
Ongoing training and professional development opportunities are essential for clerks to stay updated with industry trends and technological advancements. Employers often provide training programs to familiarize clerks with specific organizational processes and systems. Additionally, pursuing certifications in relevant fields, such as administrative support or data entry, can enhance a clerk’s skills and marketability.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
The clerk role serves as an excellent entry point into various industries and can lead to a range of career opportunities. With experience and demonstrated proficiency, clerks can advance into more specialized roles or supervisory positions. Here are some potential career paths and advancements:
Specialized Clerk Roles
Based on industry and organizational needs, clerks can specialize in specific areas. For example, in the healthcare industry, a clerk might become a medical records clerk, specializing in managing patient records and ensuring compliance with medical regulations. Similarly, in the legal field, a clerk could specialize in legal document management and court proceedings.
Supervisor or Team Lead
With experience and strong leadership skills, clerks can advance to supervisory or team lead roles. They may oversee a team of clerks, manage workflows, and ensure efficient operation of the department. This role often involves providing guidance and training to junior staff members and contributing to the development of office policies and procedures.
Office Manager or Administrative Assistant
Clerks with exceptional organizational skills and a deep understanding of office procedures can transition into office management or administrative assistant roles. These positions involve overseeing the overall administrative functions of an organization, including budgeting, personnel management, and office operations. They often require strong leadership and strategic planning skills.
Data Analyst or Data Specialist
For clerks with a strong interest in data and analytics, a career path as a data analyst or data specialist can be rewarding. With further education and specialized training, they can leverage their data management skills to interpret and analyze data, providing valuable insights to inform organizational decision-making.
Conclusion
The role of a clerk is versatile and crucial to the smooth operation of many industries. From administrative support to data management and customer interaction, clerks contribute to the efficiency and success of organizations. With the right qualifications, skills, and dedication, a clerk can advance their career and take on specialized or leadership roles, making a significant impact within their chosen industry.
What are the key responsibilities of a clerk in the healthcare industry?
+In healthcare, clerks play a vital role in managing patient records, scheduling appointments, and providing administrative support to medical staff. They ensure accurate and timely documentation, facilitate smooth patient flow, and contribute to the overall efficiency of healthcare operations.
How can clerks stay updated with technological advancements in their field?
+Clerks can stay current by participating in ongoing training programs, attending industry conferences and workshops, and utilizing online resources. Keeping up with technological trends ensures they can efficiently utilize new software and tools, enhancing their productivity and the organization’s overall performance.
What are some essential soft skills for a successful clerk?
+Effective communication, problem-solving, and time management skills are crucial for clerks. These soft skills enable them to interact professionally with colleagues and customers, resolve issues efficiently, and manage multiple tasks simultaneously, contributing to a positive and productive work environment.



