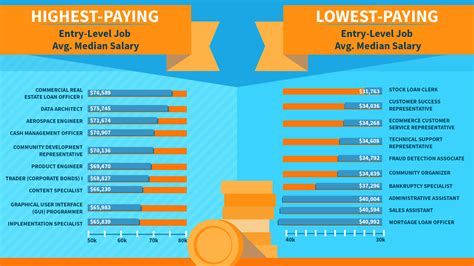
Certified Internal Auditor Jobs

In today's dynamic business landscape, the role of a Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) has become increasingly crucial for organizations across various industries. With the growing complexity of financial systems and the ever-evolving regulatory environment, companies are seeking professionals who can provide independent and objective assessments of their internal controls, risk management processes, and governance practices.
The demand for CIAs is high, and their expertise is valued by businesses of all sizes. As a CIA, you have the opportunity to work in diverse sectors, from banking and finance to healthcare and technology, ensuring the integrity and efficiency of internal operations. This article delves into the world of Certified Internal Auditor jobs, exploring the skills, responsibilities, and opportunities that await professionals in this field.
The Role and Responsibilities of a Certified Internal Auditor

A Certified Internal Auditor plays a vital role in an organization’s internal audit function. They are responsible for conducting independent and unbiased evaluations of the company’s processes, systems, and controls to identify potential risks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
The primary responsibilities of a CIA include:
- Risk Assessment: CIAs are experts in identifying and assessing various types of risks, such as financial, operational, compliance, and strategic risks. They analyze the organization's internal controls and processes to determine their effectiveness in mitigating these risks.
- Internal Audits: Conducting thorough internal audits is a core aspect of the CIA's role. They plan and execute audit engagements, designing audit programs and selecting appropriate audit techniques. This involves reviewing financial statements, examining internal processes, and evaluating compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Reporting and Communication: CIAs prepare detailed audit reports that highlight findings, recommendations, and potential areas of concern. They present these reports to management, providing clear and concise explanations of the audit results. Effective communication skills are essential to ensure that audit findings are understood and acted upon.
- Risk Management and Control: Beyond identifying risks, CIAs also assist in developing and implementing risk management strategies. They work closely with management to enhance internal controls, improve processes, and strengthen the overall governance framework.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: Detecting and preventing fraud is a critical aspect of internal auditing. CIAs are trained to identify red flags and suspicious activities, conducting forensic investigations when necessary. Their expertise helps organizations safeguard their assets and maintain ethical business practices.
Skills and Qualifications Required for CIA Jobs

To excel as a Certified Internal Auditor, certain skills and qualifications are essential. Here’s an overview of the key attributes that employers seek in CIA candidates:
- Education and Certification: A bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, business administration, or a related field is typically required. Additionally, holding the Certified Internal Auditor certification from the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) is a significant advantage. The CIA certification demonstrates a strong foundation in internal auditing principles and practices.
- Audit Experience: Relevant work experience in internal auditing or a related field is highly valued. Employers often seek candidates with a minimum of 2-5 years of experience in conducting audits, evaluating risks, and preparing audit reports.
- Technical Proficiency: CIAs should possess strong technical skills, including proficiency in accounting software, data analytics tools, and financial reporting systems. The ability to analyze large datasets and identify trends is crucial.
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Effective communication is vital for CIAs. They must be able to convey complex audit findings and recommendations to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Strong interpersonal skills are essential for building relationships and collaborating with colleagues across different departments.
- Analytical and Critical Thinking: CIAs need to have a sharp analytical mindset. They should be able to identify potential risks, evaluate internal controls, and propose practical solutions. Critical thinking skills enable them to approach complex problems with a systematic and logical mindset.
- Professionalism and Ethics: Maintaining the highest level of professionalism and ethical conduct is paramount for CIAs. They must adhere to the IIA's Code of Ethics and demonstrate integrity, objectivity, and independence in their work.
Job Opportunities and Career Progression
The field of Certified Internal Auditing offers a wide range of job opportunities and career paths. Here are some common roles and potential career trajectories for CIAs:
Entry-Level Internal Auditor
Entry-level internal auditors are often fresh graduates or individuals with 1-2 years of relevant experience. They assist senior auditors in conducting audits, gaining hands-on experience in various aspects of internal auditing. This role provides a solid foundation for future career growth.
Senior Internal Auditor
As CIAs gain experience and demonstrate their expertise, they can advance to senior internal auditor positions. Senior auditors take on more complex audit engagements, leading and managing audit teams. They are responsible for ensuring the quality and accuracy of audit reports and providing strategic insights to management.
Internal Audit Manager
Internal audit managers oversee multiple audit teams and are responsible for the overall internal audit function within an organization. They develop and implement the audit plan, allocate resources, and mentor junior auditors. This role requires strong leadership skills and a deep understanding of the organization’s business objectives.
Director of Internal Audit
Directors of internal audit are senior-level professionals who provide strategic direction and oversight to the internal audit function. They report directly to the organization’s executive leadership, advising on risk management, compliance, and internal control matters. Directors often have extensive industry experience and a proven track record of success in internal auditing.
Chief Audit Executive (CAE)
The Chief Audit Executive is the top-level position in the internal audit department. CAEs are responsible for the overall performance and effectiveness of the internal audit function. They set the strategic direction, establish relationships with the board of directors, and ensure the department aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives. CAEs often have a strong background in internal auditing, risk management, and leadership.
Benefits and Challenges of Certified Internal Auditor Jobs
Certified Internal Auditor jobs offer numerous benefits and present unique challenges. Let’s explore some of the key aspects:
Benefits
- Job Security: With the increasing focus on corporate governance and regulatory compliance, the demand for CIAs is likely to remain high. Their expertise is valuable to organizations, ensuring job security and stable career prospects.
- Diverse Industry Exposure: CIAs have the opportunity to work in various industries, gaining exposure to different business models and operational complexities. This diverse experience enhances their skills and broadens their professional network.
- Professional Development: The internal auditing field offers continuous learning and professional growth. CIAs can pursue advanced certifications, such as the Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE) or Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), to further specialize their skills.
- Impactful Work: CIAs play a crucial role in improving an organization’s internal processes, risk management, and governance. Their work directly contributes to the overall effectiveness and success of the business, providing a sense of accomplishment.
Challenges
- Constant Learning: The internal auditing field is dynamic, with evolving regulations and technologies. CIAs must stay updated with industry trends, new audit techniques, and emerging risks. Continuous learning is essential to remain effective and relevant.
- Time and Resource Constraints: Internal audit engagements often have tight deadlines and limited resources. CIAs need to manage their time effectively, prioritize tasks, and make efficient use of available resources to deliver high-quality audit reports within the allocated timeframe.
- Ethical Dilemmas: CIAs may encounter ethical dilemmas, especially when dealing with sensitive information or potential fraud cases. Maintaining objectivity, independence, and confidentiality is crucial to uphold the integrity of the internal audit function.
Future Outlook and Industry Trends
The future of Certified Internal Auditor jobs looks promising, driven by several key factors and industry trends:
- Regulatory Compliance: With increasing regulatory requirements and compliance standards, organizations will continue to rely on CIAs to ensure they meet legal and ethical obligations. The demand for CIAs will remain high as businesses strive to maintain compliance.
- Technology Integration: The adoption of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, is transforming the internal auditing landscape. CIAs who possess strong technical skills and can leverage these technologies will be highly sought after.
- Risk-Based Auditing: The focus on risk-based auditing is expected to continue. CIAs who can identify and assess emerging risks, such as cybersecurity threats and data privacy concerns, will be valuable assets to organizations.
- Sustainability and ESG Auditing: As sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations gain prominence, CIAs with expertise in these areas will be in demand. Auditing sustainability practices and ensuring organizations meet their ESG commitments will become increasingly important.
- Remote Work and Virtual Auditing: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work and virtual auditing practices. CIAs who can adapt to these new working environments and utilize remote auditing tools will be well-positioned for future opportunities.
Conclusion
Certified Internal Auditor jobs offer a rewarding and challenging career path for professionals with a passion for risk management, governance, and internal controls. As organizations continue to prioritize ethical practices and regulatory compliance, the demand for skilled CIAs will remain strong. By acquiring the necessary skills, certifications, and experience, individuals can embark on a successful journey in the field of internal auditing, making a meaningful impact on organizations and contributing to their long-term success.
What is the typical salary range for Certified Internal Auditors?
+The salary range for Certified Internal Auditors can vary depending on factors such as experience, industry, and location. On average, entry-level CIAs can expect to earn between 50,000 and 70,000 annually. With experience and advancement, senior-level CIAs can earn upwards of $100,000 or more.
How long does it take to become a Certified Internal Auditor (CIA)?
+The timeline to become a CIA depends on several factors. Typically, it takes around 2-3 years to complete the educational and experience requirements. Candidates need to have a bachelor’s degree and at least two years of internal auditing experience. Once eligible, the certification process involves passing the CIA exams, which consist of three parts.
What are the key benefits of pursuing a career as a Certified Internal Auditor?
+Pursuing a career as a CIA offers several benefits, including job security, diverse industry exposure, and the opportunity to make a tangible impact on organizations. CIAs also have the advantage of continuous professional development and the potential for advancement into senior leadership roles.